
A recent spill covered Orange County’s beaches in oil. Who will pay to clean it up?
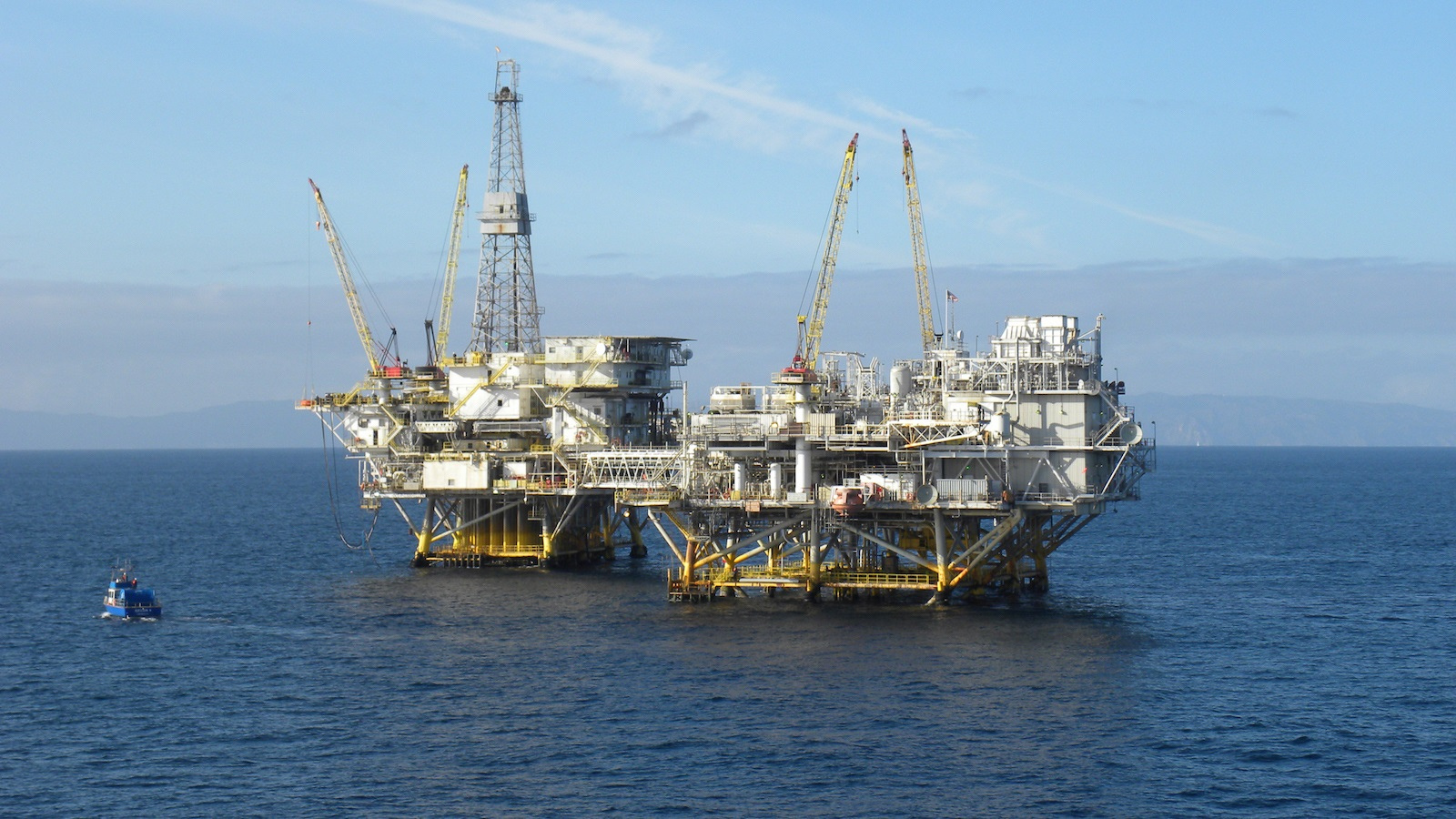

Earlier this month, we saw another devastating oil spill spew thousands upon thousands of gallons of oil into the Pacific Ocean a couple of miles off of the coast of Southern California. The spill was an environmental disaster, shutting down beaches, killing wildlife, and potentially harming the health of the residents of Orange County.
The investigation into why the spill occurred is still ongoing. It appears a ship’s anchor struck and dragged the pipeline that later leaked, though it’s still unclear whether that caused the spill or not. Amplify Energy Corp, the Houston-based oil company that owns the pipes where the spill originated, has apparently had non-compliance and diligence issues for years after emerging from bankruptcy in 2017. Amplify has been working on upgrading its aging infrastructure, but, according to reporting, has also been planning to initiate new drilling in the area. A company with a history of regulatory violations planning new drilling is troubling.
Even more troubling is that it appears that the spill started sometime on Friday, October 1, but the company didn’t shut down operations until the next night, more than 24 hours later. In the meantime, millions of people went to the affected beaches.
However the spill happened, whether it was a problem with Amplify’s pipes or an anchor from a ship striking the pipeline, companies who decide to take on the risk of drilling should be required to pay for the cleanup costs. The oil companies should also pay for environmental damages and other economic losses. But do they?
Under federal law, companies who drill are responsible for these costs — or at least some of them. The Oil Pollution Act of 1990 requires responsible parties to pay for the damages caused by the oil spill, yet their liability is capped at removal costs plus up to a little over $137 million in damages (although courts retain the ability to waive the cap). This means that, realistically, oil companies do not always bear full responsibility for the overall damage caused. While the Orange County spill probably won’t amass costs that reach the liability cap, larger spills like the BP Deepwater Horizon spill in the Gulf of Mexico, caused $17.2 billion in damages in environmental harms alone.
Under current tax laws, oil companies can claim tax credits on up to 35% of their losses. BP saved nearly $10 billion on their tax bill by deducting costs related to the Deepwater Horizon spill. Indirectly, this tax credit put taxpayers on the line for some of the costs of BP’s oil spill.
In the case of the Orange County spill, the polluter, whoever it may be, should technically pay here — at least for clean up and direct damages. But what if, for whatever reason, the company can’t afford to?
In the case of Fieldwood Energy, another Houston-based oil company, declaring bankruptcy could potentially offload billions of dollars of clean-up costs onto U.S. taxpayers. Citing the downturn in energy demand due to the pandemic as its cause to file its second bankruptcy in 2020, Fieldwood is attempting to abandon multiple offshore oil platforms and pipelines in an attempt to stay afloat. However, deserting these platforms means taxpayers could be shouldering the environmental clean-up costs of properly decommissioning these assets. Feildwood’s plan has since been approved, raising concerns that it may pave the way for other companies to file for bankruptcy in order to cut costs.
To avoid taxpayers taking the fall for offshore oil spills, the U.S. Coast Guard administers a trust fund largely paid for by a fee on every barrel of oil. But this all raises the larger question: Shouldn’t we require companies to prove they have the means to cover the costs of a spill before they drill? Beyond the regulatory cap, oil companies should be required to show they can pay for the full cost of clean-up as well as environmental, economic and other societal damages.
Oil drilling is a risky business. When we drill, we spill: Thousands of spills occur in U.S. waters every year. Most aren’t as big as the spill last weekend in California, but even the small ones can cause serious damage. The big ones, on the other hand, cause catastrophic damage. Consider this: A 2017 underwater dive in the Gulf of Mexico showed areas still essentially dead from the Deepwater Horizon spill, a full six years after the spill. If the polluters aren’t paying for those damages, in one way or another, the rest of us are.
While we continue drilling oil (and yes, we need to stop) we should ensure the costs reflect the full extent of the damages it causes. Right now it doesn’t, and that’s why we’re still drilling, and spilling, so much.
Topics
Authors
Jenn Engstrom
State Director, CALPIRG
Jenn directs CALPIRG’s advocacy efforts, and is a leading voice in Sacramento and across the state on protecting public health, consumer protections and defending our democracy. Jenn has served on the CALPIRG board for the past two years before stepping into her current role. Most recently, as the deputy national director for the Student PIRGs, she helped run our national effort to mobilize hundreds of thousands of students to vote. She led CALPIRG’s organizing team for years and managed our citizen outreach offices across the state, running campaigns to ban single-use plastic bags, stop the overuse of antibiotics, and go 100% renewable energy. Jenn lives in Los Angeles, where she enjoys spending time at the beach and visiting the many amazing restaurants in her city.
Find Out More
Expired: How date labels drive food waste and hunger

2024 Program Agenda

Lawn care goes electric

